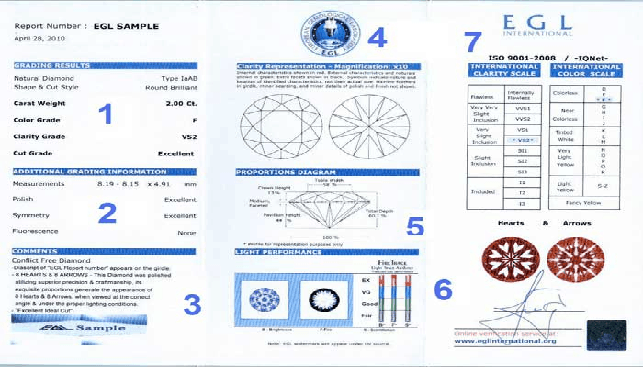
Many customers buying diamond jewelry (or these days, even loose diamonds, given the preponderance of diamond wholesalers on the Internet) are aware of the main parameters of diamond grading – cut, color, and clarity, as well as the diamond’s exact carat weight and cut. But most end customers don’t have the technical expertise to examine a stone for themselves and must rely on a diamond’s certificate.
Diamonds and other gemstones can be certified by a number of gemological laboratories, but two of the best known are non-profit organizations in the gemstone and diamond industry that also serve as research institutes in the field of gemology – the American Gem Society (AGS) and the Gemological Institute of America (GIA).
The AGS offers a number of reports providing information on gemstone grade, depending on what information is required. AGS grades clarity using the common industry grades and uses a color scale that ranges from 1-10. The AGC uses one of six grades to assess a diamond’s cut – from the trademarked term AGS Ideal to Poor.
Like the AGS, the GIA provides different reports. But the GIA grades diamond color using a D-Z letter scale. D denotes a colorless diamond and Z indicates a visible yellow hue. The GIA D-Z scale applies only to white diamonds, as fancy colored diamond are assigned terms that also describe the saturation and overtones of the stone’s color, for example “Fancy Vivid Purplish-Pink.”
HRD Antwerp, one of the major European gemological laboratories, seals its certified diamonds in the certificate itself – ensuring that the stone and its certificate stay together, as well as allowing the buyer to see the diamond’s main particulars at a glance. This method is in high demand in Asia, and HRD has recently expanded its sealing services through a Hong Kong lab.
Advances in gemological technology have made it possible to provide visual documentation of a diamond along with the written certificate. Computerized diamond analysis systems offer customers detailed diagrams of a diamond’s inclusions (internal flaws) in either printed or digital format along with images of the stone.